Best Practices for Clinical Trials and Data Management
Clinical trials are the backbone of medical advancements, ensuring that new treatments are both safe and effective. As we progress into 2025, the complexity of these trials has increased, necessitating robust data management practices. This comprehensive guide delves into the best practices for clinical trials and data management, focusing on data validation and cleaning, data security, real-time monitoring, and effective communication across teams.
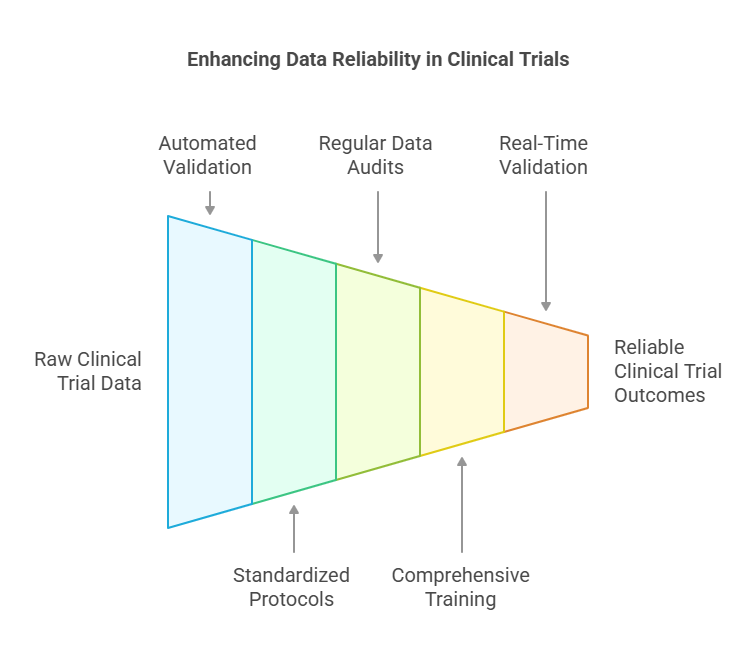
Data Validation and Cleaning:
Accurate and complete data is paramount in clinical trials. Data validation and cleaning are critical processes that ensure the reliability of trial outcomes.
Key Strategies:
Automated Validation Tools: Implementing automated systems can detect inconsistencies and errors in real-time, reducing manual workload and enhancing accuracy.
Standardized Protocols: Utilizing global data standards, such as CDISC, ensures consistency across multi-site trials.
Regular Data Audits: Conducting periodic audits helps identify discrepancies early, maintaining data integrity.
Comprehensive Training: Equipping data managers with thorough training ensures effective handling of validation tools and adherence to protocols.
Real-Time Validation: Integrating real-time validation tools, especially for data from wearable devices, ensures immediate detection of anomalies.
Related Blog: The Role of Data Management in Successful Clinical Trials
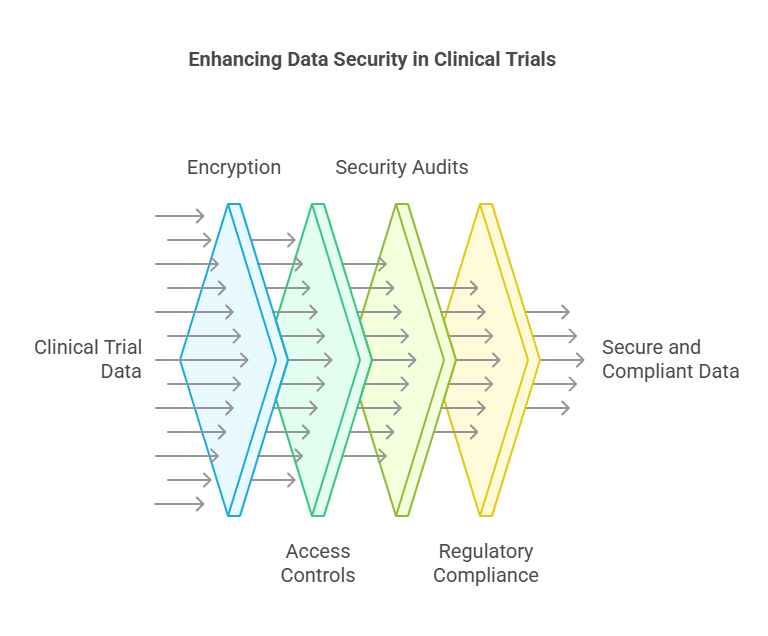
Data Security:
With the increasing digitization of clinical trials, safeguarding patient data has become more critical than ever. Ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA and GDPR is essential.
Essential Measures:
Encryption: Implementing encryption for data at rest and in transit protects against unauthorized access.
Access Controls: Utilizing role-based access controls and multi-factor authentication ensures that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
Regular Security Audits: Conducting frequent audits helps identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities.
Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to standards like 21 CFR Part 11, HIPAA, and GDPR ensures legal compliance and builds trust.
Real-Time Monitoring:
Real-time monitoring enhances the efficiency and safety of clinical trials by allowing immediate detection and resolution of issues.
Advantages:
Immediate Data Access: Electronic Data Capture (EDC) systems provide real-time data entry and validation, reducing errors.
Enhanced Patient Safety: Continuous monitoring allows for prompt responses to adverse events, ensuring participant well-being.
Improved Data Quality: Real-time validation ensures data accuracy and completeness from the outset.
Relevant Blog: How to Choose the Right Clinical Trial Management Software?
Communication Across Teams:
Effective communication among stakeholders is vital for the success of clinical trials. Ensuring that data is accessible and understandable facilitates collaboration and informed decision-making.
Best Practices:
Centralized Data Platforms: Utilizing unified platforms ensures that all team members have access to the same data, reducing discrepancies.
Regular Meetings and Updates: Scheduled discussions keep all stakeholders informed and aligned on trial progress.
Standardized Reporting: Consistent data presentation formats enhance clarity and comprehension across teams.
Training and Support: Providing ongoing education ensures that all team members can effectively utilize data management tools.
Relevant Blog: Top 5 Clinical Trial Data Management Strategies You Should Know
10 Lesser-Known Facts About Clinical Trials and Data Management
Blockchain Integration: Blockchain technology is being explored to enhance data integrity and transparency in clinical trials. (Source)
AI-Powered Monitoring: Artificial Intelligence is increasingly used for real-time monitoring, predicting potential issues before they arise. (Source)
Wearable Devices: The use of wearables provides continuous data, improving the accuracy of trial outcomes. (Source)
Decentralized Trials: Remote trials have become more prevalent, increasing participant diversity and convenience.
Patient-Centric Approaches: Emphasizing patient experience enhances recruitment and retention rates.
Adaptive Trial Designs: Flexible trial structures allow modifications based on interim results, improving efficiency.
Real-World Data Utilization: Incorporating data from real-world settings enhances the applicability of trial findings.
Regulatory Sandboxes: Some regions offer controlled environments to test innovative trial methods without full regulatory constraints.
Digital Twins: Simulated models of patients are used to predict responses to treatments, reducing the need for extensive trials.
Gamification: Incorporating game elements into trials can improve participant engagement and data collection.
Explore Courses for Clinical Research Career
Courses Available:
Conclusion
In 2025, clinical trials continue to evolve rapidly with advancements in digital tools and data standards. Applying best practices in data validation, data security, real-time monitoring, and inter-team communication ensures the integrity, safety, and success of every trial phase. Organizations that prioritize these areas not only comply with global regulations but also gain valuable insights and streamline development timelines.
At CCRPS, we are committed to supporting researchers and clinical professionals with the most current training, tools, and resources in clinical trial management and data handling. Whether you're leading a global study or a local pilot trial, our expertise ensures you stay compliant, efficient, and ahead of the curve.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Data validation ensures the accuracy, reliability, and completeness of trial data. It helps detect inconsistencies, missing values, or errors early in the process, which is critical for regulatory approvals and scientific integrity.
-
Compliance involves encrypting patient data, securing storage, restricting access, maintaining audit trails, and informing participants of their rights regarding data usage and privacy.
-
Real-time monitoring enables faster responses to protocol deviations or adverse events, reduces risks to participants, and improves data quality by catching errors as they occur.
-
Some of the common challenges include misalignment on protocols, data misinterpretation, delays in sharing updates, and lack of access to centralized platforms for all stakeholders.