The Role of Data Management in Successful Clinical Trials
Data management stands as the fundamental foundation of clinical trials because it enables efficient trials that produce useful results. The healthcare and pharmaceutical industries conduct clinical trials which depend on well-organized high-quality data to evaluate medical treatments regarding safety and effectiveness and dosage. When data management fails it produces incorrect results while missing valuable opportunities and potentially leading to non-compliance with regulatory requirements.
This blog examines data management in clinical trials by explaining its essential functions and challenges and its role in enhancing decision-making and trial success. The article examines how data management techniques are advancing in 2025 to maintain accurate and timely clinical trial results.
Data as the Backbone of Clinical Trials
The collection of data in clinical trials requires gathering extensive information from multiple sources. The data gathered throughout a clinical trial serves as the foundation for decision-making because it includes patient demographics and baseline measurements as well as drug dosages and side effects. The trial's success depends on maintaining accurate and timely data that remains actionable.
Data serves as the backbone of clinical trials for several key reasons.
Foundation for Decision-Making: The decisions about trial continuation or termination rely on data as their essential base. The quality of these decisions depends directly on the accuracy and completeness of the data.
Regulatory Compliance: The clinical trials are governed by the strict regulatory guidelines of the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) or EMA (European Medicines Agency). It is therefore important to well manage the data in order to meet these regulatory standards and be able to get the trial approved.
Patient Safety: The proper collection of adverse events or reactions through proper data management is important in order to protect the patient safety and to prevent any untoward incidents during the trial.
Key Data Management Functions
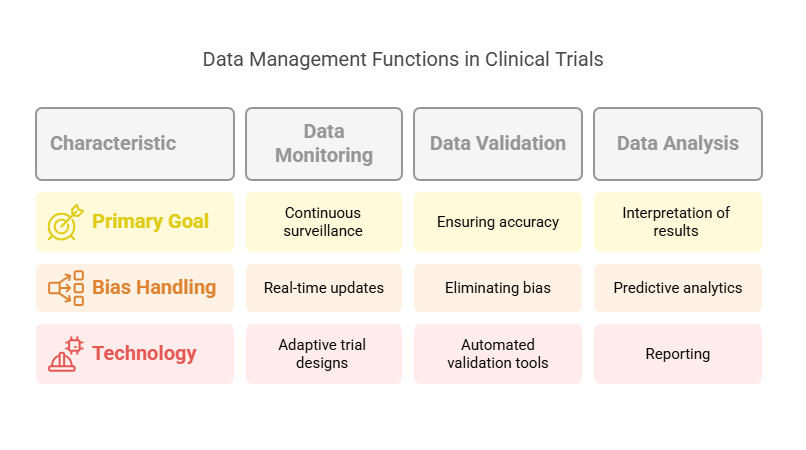
The quality and integrity of collected data in clinical trials depends on various data management functions. The trial's success depends on three essential functions: data monitoring, validation, and analysis.
Data Monitoring:
Continuous Surveillance: The clinical trial uses data monitoring to guarantee that all collected data remains consistent, accurate and timely. Monitoring is essential for detecting and resolving any discrepancies or irregularities that may occur during the trial.
Real-Time Updates: Real-time patient data monitoring through advanced systems allows medical staff to immediately detect problems including adverse events and protocol violations.
Adaptive Trial Designs: Researchers can modify the trial’s design based on data collection to achieve objectives while maintaining safety and efficiency.
Data Validation:
Ensuring Accuracy: Data validation confirms that collected data remains accurate and complete and reliable. The process of data validation requires both consistency checks and logical coherence assessments to remove errors which stem from manual entry and instrumentation and patient-reported outcomes.
Eliminating Bias: Data validation helps to eliminate biases that may occur from incorrect data collection methods. This makes sure that results are credible and valid, which in turn supports the overall integrity of the trial.
Automated Validation Tools: The adoption of AI-powered automated data validation tools shows growing momentum for 2025. The tools detect inconsistencies and resolve them at a speed that surpasses conventional methods.
Data Analysis:
Interpretation of Results: After validation, the data must be analyzed to interpret the results of the trial. This includes statistical analysis, identifying trends, and drawing conclusions that can inform decision-making.
Predictive Analytics: The implementation of machine learning and AI technologies has increased the popularity of predictive analytics in clinical trials. The technology enables researchers to foresee results and enhance trial designs before investing substantial resources.
Reporting: Data analysis remains unfinished until reports deliver precise and useful information. The reports serve as the final output of the study which is presented to the stakeholders including the sponsors and regulatory bodies to evaluate the trial's progress and results.
Challenges in Data Management
Data management remains essential for clinical trials yet it encounters multiple obstacles. The challenges affect both the speed and precision and dependability of data collection. The success of any clinical trial depends on solving these problems.
Poor Quality Data:
Inaccurate Patient Data: Mistakes in patient information or inconsistent data recording can affect the quality of the trial's findings. For example, incorrect dosages or misreported adverse events can skew results.
Data Duplication: In some cases, data can be duplicated or incorrectly entered, leading to redundancies that compromise the overall integrity of the dataset.
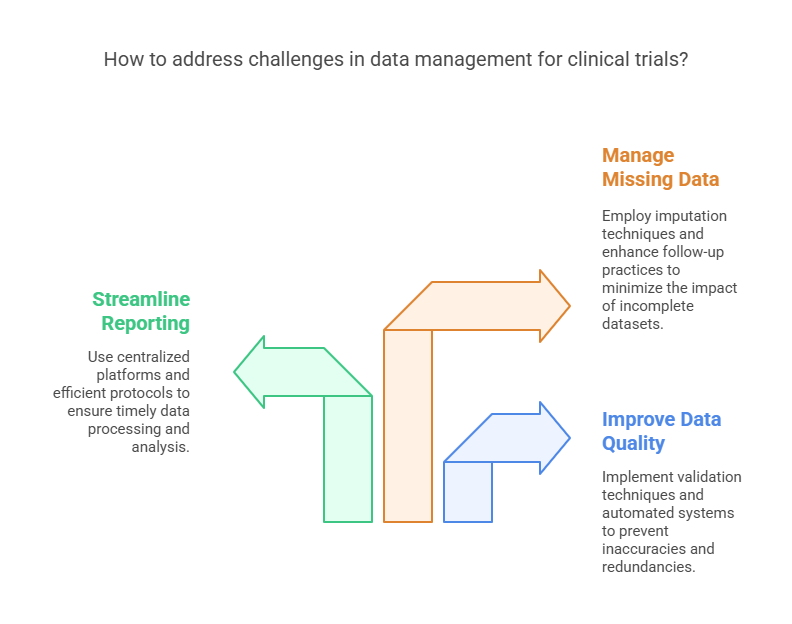
Mitigation: Modern clinical trials leverage advanced data validation techniques, real-time data monitoring, and automated systems to prevent poor-quality data.
Delays in Reporting:
Slow Data Processing: In large-scale clinical trials, the sheer volume of data can delay reporting. This can be problematic, as decision-makers rely on up-to-date information to make informed choices about the continuation or adjustment of the trial.
Timeliness of Adverse Event Reporting: Delays in reporting adverse events can compromise patient safety and delay regulatory approval.
Mitigation: Implementing centralized data management platforms and streamlining reporting protocols can help ensure timely data processing and analysis.
Missing Data:
Incomplete Data Sets: Missing or incomplete data can create gaps in the trial results. Whether due to patient dropout, lost records, or logistical issues, missing data can severely impact the overall conclusions.
Patient Dropout: Patients may drop out of trials for various reasons, and managing missing data due to these withdrawals is a constant challenge.
Mitigation: Strategies such as imputation techniques (filling in missing data based on statistical models) and improved follow-up practices can help reduce the impact of missing data.
How Data Management Enhances Decision-Making and Outcomes
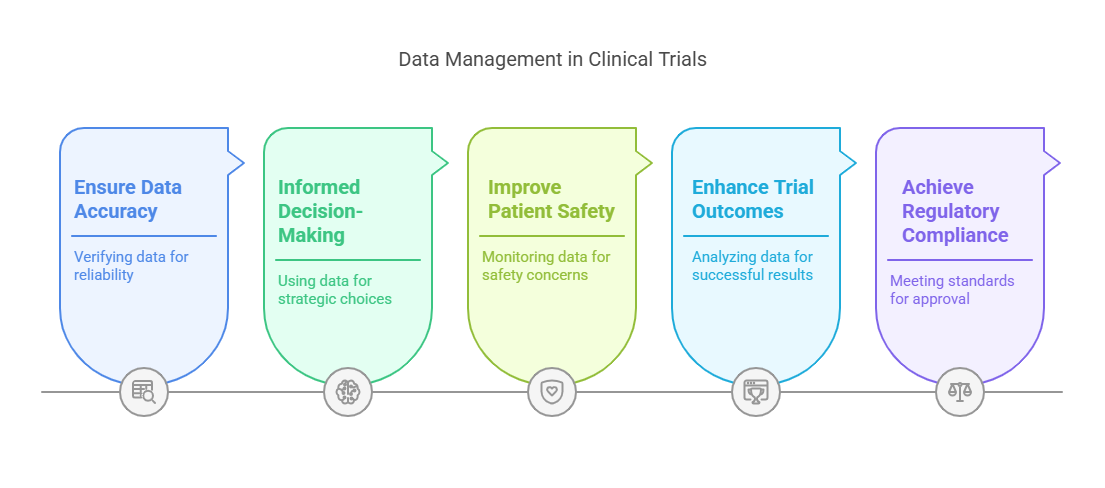
Effective data management plays a key role in enhancing decision-making and improving clinical trial outcomes. By ensuring that the data is accurate, complete, and timely, researchers can make well-informed decisions that ultimately benefit patients and the healthcare industry.
Informed Decision-Making:
With reliable data, stakeholders can make better decisions about patient safety, trial design adjustments, and early termination of trials if necessary. The ability to act on accurate data enables researchers to mitigate risks and optimize trial efficiency.
Real-time data access allows sponsors to make quick decisions, especially in adaptive clinical trial designs that respond to interim results.
Improved Patient Safety:
The careful monitoring and validation of data ensure that any adverse events or safety concerns are identified early in the trial. This helps reduce the risk to patients and ensures compliance with ethical standards.
Better Trial Outcomes:
Data-driven decision-making results in more robust trial outcomes. With accurate data analysis, researchers can determine the optimal dosages, treatment protocols, and patient profiles, increasing the likelihood of successful trial results.
Regulatory Compliance:
High-quality data management practices ensure that clinical trials meet regulatory standards, which is essential for securing approval from bodies like the FDA or EMA. Properly managed data simplifies the regulatory submission process and ensures smooth approval.
10 Lesser-Known Facts About Data Management in Clinical Trials
Data Integration: Modern clinical trials often integrate data from various sources, including electronic health records (EHRs), lab results, and wearable devices. (Source)
AI in Monitoring: Artificial intelligence is being increasingly used for data monitoring to identify patterns and predict potential trial issues before they occur. (Source)
Blockchain for Data Security: Blockchain technology is being explored to secure clinical trial data and prevent tampering or unauthorized access. (Source)
Patient-Reported Data: Many trials now include patient-reported outcomes (PROs), which can provide valuable real-time insights into the patient's experience. (Source)
Mobile Health Technologies: Wearables and mobile health technologies are increasingly used to collect continuous, real-time data from participants, enhancing trial accuracy.
Automated Data Cleaning: Automation is reducing the time and cost involved in data cleaning by identifying discrepancies and inconsistencies in data early.
Adaptive Trial Designs: Adaptive trial designs, facilitated by real-time data monitoring, allow researchers to modify trials as they progress based on interim results. (Source)
Data Standardization: Data standardization helps ensure that information collected across different sites and devices is comparable, which is critical for large-scale trials.
Role of Big Data: Big data analytics is transforming clinical trials by providing insights from vast datasets, accelerating the process of identifying successful treatments.
Remote Monitoring: With the rise of decentralized clinical trials, data management includes remote monitoring tools that enable researchers to track patient progress without in-person visits.
Related Blogs
How to Choose the Right Clinical Trial Management Software?
Why Clinical Trial Management is Essential for Pharma Companies?
Key Challenges in Clinical Trial Data Management
Explore Courses for Clinical Research Career
Courses Available:
Conclusion
In conclusion, data management is the heart of successful clinical trials. As clinical trials grow increasingly complex and data-driven, the role of data management becomes even more vital. With robust data monitoring, validation, and analysis, researchers can overcome challenges such as poor-quality data, delays in reporting, and missing information. By making data more accurate, timely, and actionable, data management enhances decision-making and improves patient safety, ultimately leading to more successful clinical trial outcomes.
At CCRPS, we recognize the importance of effective data management in clinical trials. With our expertise in clinical research, we are committed to ensuring that data is not only collected but also managed with the highest standards of accuracy and timeliness to ensure better outcomes.
-
Data management ensures that clinical trials are based on accurate, timely, and actionable data. It plays a crucial role in decision-making, patient safety, and regulatory compliance.
-
The key functions include data monitoring, validation, and analysis. These processes ensure the quality and integrity of data collected during the trial.
-
Challenges include poor quality data, delays in reporting, and missing data, all of which can impact the accuracy and timeliness of trial results.
-
By providing accurate, up-to-date information, data management helps stakeholders make informed decisions about patient safety, trial design, and overall outcomes.
-
In 2025, advancements like AI-powered data validation tools, predictive analytics, and real-time monitoring systems will continue to improve the accuracy and efficiency of data management in clinical trials.