How Hospitals Use Medical Monitoring to Save Lives?
In the fast-paced environment of modern healthcare, medical monitoring systems are indispensable tools that enable hospitals to deliver timely and effective care. Particularly in Intensive Care Units (ICUs) and Emergency Rooms (ERs), these systems provide real-time data on patients' vital signs, facilitating prompt interventions that can be life-saving. This comprehensive guide explores the critical role of medical monitoring in hospitals, highlighting the technologies involved, their benefits, and emerging trends shaping patient care in 2025.
Understanding Medical Monitoring in Hospitals
Medical monitoring involves the continuous observation of a patient's physiological parameters, such as heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate. Advanced monitoring systems collect, analyze, and display this data, allowing healthcare professionals to detect early signs of deterioration and respond swiftly. These systems are particularly vital in ICUs and ERs, where patients often require immediate and intensive care.
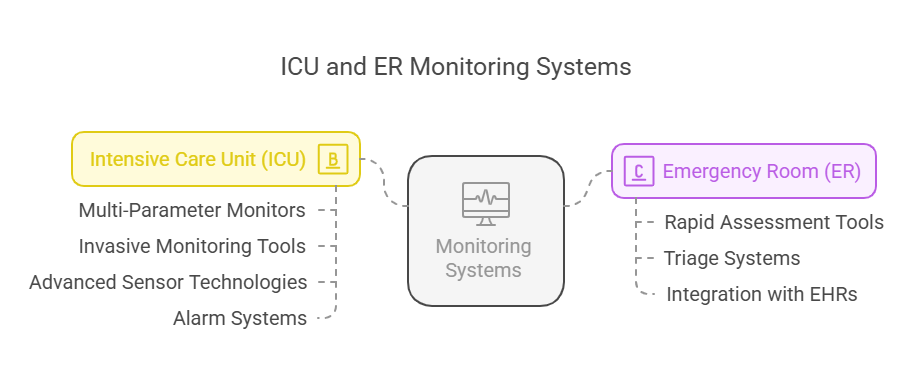
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) Monitoring
ICUs cater to critically ill patients who need constant supervision. Key components of ICU monitoring include:
Multi-Parameter Monitors: Devices that track various vital signs simultaneously, providing a comprehensive view of a patient's condition.
Invasive Monitoring Tools: Such as arterial lines for continuous blood pressure measurement and central venous catheters for assessing fluid status.
Advanced Sensor Technologies: Innovations like Meta4ICU integrate AI and machine learning to predict patient deterioration by analyzing trends over time.
Alarm Systems: Configurable alerts notify staff of critical changes, though managing false alarms remains a challenge.
Emergency Room (ER) Monitoring
ERs handle patients with acute conditions requiring immediate attention. Monitoring in ERs focuses on:
Rapid Assessment Tools: Portable monitors for quick evaluation of vital signs upon patient arrival.
Triage Systems: Prioritize patients based on the severity of their condition, often using scoring systems integrated into monitoring software.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Ensures that patient data is readily available to all relevant departments.
Related Blog: Top 10 Everyday Devices That Use Medical Monitoring
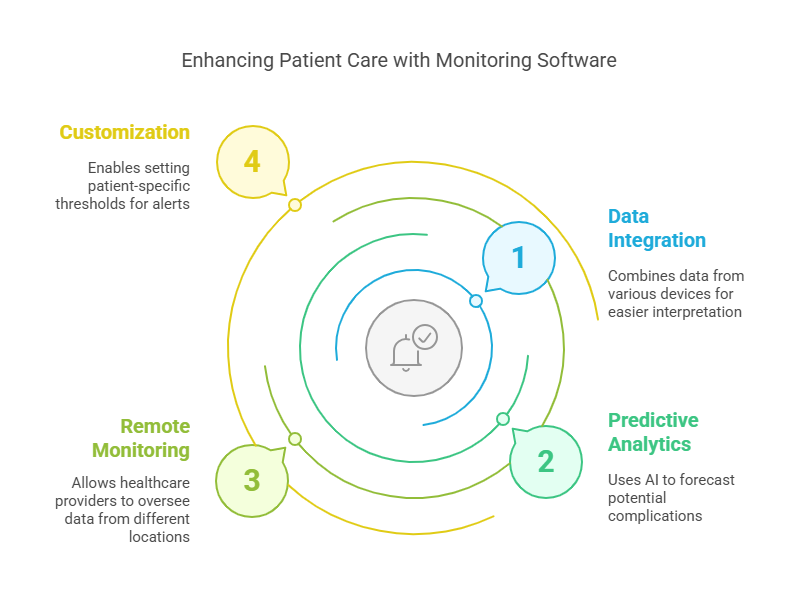
Monitoring Software: Enhancing Patient Care
Modern monitoring software plays a pivotal role in patient care by:
Data Integration: Combining information from various devices into a unified interface for easier interpretation.
Predictive Analytics: Utilizing AI to forecast potential complications, allowing for preemptive interventions.
Remote Monitoring: Enabling healthcare providers to oversee patient data from different locations, which is especially beneficial in resource-limited settings.
Customization: Allowing clinicians to set patient-specific thresholds for alerts, reducing the incidence of false alarms.
Benefits of Advanced Monitoring Systems
Implementing sophisticated monitoring systems in hospitals offers numerous advantages:
Improved Patient Outcomes: Continuous monitoring facilitates early detection of issues, leading to timely treatments and better recovery rates.
Operational Efficiency: Streamlined workflows and reduced manual data entry free up staff to focus more on patient care.
Cost Savings: Early interventions can prevent complications, reducing the length of hospital stays and associated costs.
Enhanced Patient Safety: Real-time data and alerts help prevent medical errors and adverse events.
Emerging Trends in Medical Monitoring (2025)
The landscape of medical monitoring is continually evolving. Notable trends include:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI algorithms are increasingly used to analyze complex datasets, improving diagnostic accuracy and predicting patient deterioration.
Wearable Technology: Devices that allow for continuous monitoring of patients outside traditional hospital settings, promoting proactive health management.
Telemedicine Expansion: Remote monitoring capabilities support telehealth services, extending care to patients in remote or underserved areas.
Enhanced Data Security: With the rise in digital health data, robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect patient information.
Related Blog: How Technology Is Changing the Way We Monitor Health
Lesser-Known Facts About Medical Monitoring
AI in Fetal Monitoring: In Malawi, AI-enabled fetal monitoring software has significantly reduced stillbirths and neonatal deaths by providing continuous real-time monitoring during labor. (Source)
Smart Hospitals: The concept of 'smart hospitals' is gaining traction, with facilities integrating AI, IoT, and robotics to enhance patient care and operational efficiency. (Source)
Staff Safety Technologies: Hospitals are adopting location-tracking badges for staff, improving safety and operational efficiency by automating administrative tasks. (Source)
Predictive Maintenance: AI is used not only for patient monitoring but also for predicting equipment failures, ensuring timely maintenance and reducing downtime.
Customized Alerts: Modern systems allow for patient-specific alert settings, reducing alarm fatigue among healthcare providers.
Integration with Mobile Devices: Some monitoring systems now offer mobile integration, allowing clinicians to receive alerts and patient data on their smartphones.
Environmental Monitoring: Beyond patient vitals, some systems monitor environmental factors like room temperature and air quality, contributing to patient comfort and safety.
Data Analytics for Resource Allocation: Hospitals use data from monitoring systems to optimize resource allocation, such as staffing and bed management.
Patient Engagement Tools: Certain monitoring platforms include features that engage patients in their care.
Explore Courses for Clinical Research Career
Courses Available:
Conclusion
Medical monitoring systems have revolutionized hospital care, especially in ICUs and ERs, by enabling real-time tracking of vital signs and early detection of critical changes in patient conditions. As we advance through 2025, the integration of AI, predictive analytics, and wearable technology continues to strengthen patient safety, improve outcomes, and streamline hospital operations. These innovations mark a significant shift toward proactive, data-driven healthcare. At CCRPS, we are committed to supporting this transformation by providing advanced training and certification programs that empower medical professionals to effectively utilize monitoring technologies and save more lives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
In 2025, ICUs and ERs commonly use multi-parameter monitors, cardiac monitors, pulse oximeters, capnography systems, and invasive pressure monitors. These systems track heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and more in real-time. Many of them are now integrated with AI-based software and electronic health records (EHRs) to provide smarter, faster responses to changes in a patient's condition.
-
Artificial intelligence enhances medical monitoring by analyzing large volumes of patient data to identify subtle patterns that may indicate early signs of deterioration. In 2025, AI is also used for predictive analytics, helping clinicians anticipate complications like sepsis or cardiac arrest before they become critical. AI-driven systems reduce false alarms and provide clinical decision support, increasing accuracy and response speed in emergency situations.
-
Yes. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) has become a core feature of modern hospitals, especially with the rise of smart beds and wearable sensors. Clinicians can monitor patients' vitals from centralized nursing stations or even off-site, improving care in isolation units, post-operative recovery, and during pandemics. This is especially useful in rural or understaffed facilities where specialists may not always be on-site.
-
Data security has become a top priority in 2025. Most hospital monitoring systems are now equipped with advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and blockchain-based data logging to ensure patient data remains secure and tamper-proof. Additionally, updated healthcare regulations and compliance frameworks, like HIPAA 2.0 in the U.S., mandate stricter oversight on patient data access and storage.