Pharmaceutical and Contract Research Organization Employee Training
Pharmaceutical companies are facing the growing stressful task of delivering better results at lower costs and in shorter time while fulfilling the growing number of guidelines and regulations (including ICH GCP and Clinical Trial Directive). This is a very big burden on the technical and technical skill base of all organisations, whether they are large, medium or small.
They are certification courses, and certain coaches and managers are CCRPS accountable for developing clinical study employees are now facing the necessity to provide faster, stronger and longer lasting coaching solutions. It isn't only the current gaps that these solutions have to address, but they also has to develop “World class” decibels.
Although the size of the business may be restricted, there may be limited resources available to spend on training clinical study staff. Hence the investment in training has to be targeted to providing worthwhile training options that strategically enhance clinical research operation.
It may be a good idea to call for a limitation of the funds that could be useful for the development and effective implementation of a pharmaceutical practice plan. It is not just a good response for the staff to enroll in publicly available courses. Instead, it may involve the development of a internal training plan that would be more solid and robust in the presence of the everyday stress that is encountered during the course of clinical development applications. Such pressures can be overwhelming and sometimes erase any possible value of off-the-job training as employees may not be able to fully implement what they have learned.
This report shows that a training plan is important in order to keep and gain the full value of important training interventions. Furthermore, the training approach has to be properly sourced—definitely not the easiest, most obvious solution available on the market.
A"Training Plan" could be described as value-added, prioritized and readily-implementable strategy for addressing both present and future performance openings.
A training approach is alignment of the people goals with the organizational and business goals. The training plan has to be dynamic in order to incorporate changes in the business as well as external changes (for example, the new regulations affecting drug development such as the Clinical Trial Directive, the ICH electronic common technical document, and the increasing Phamacovigilance requirements.
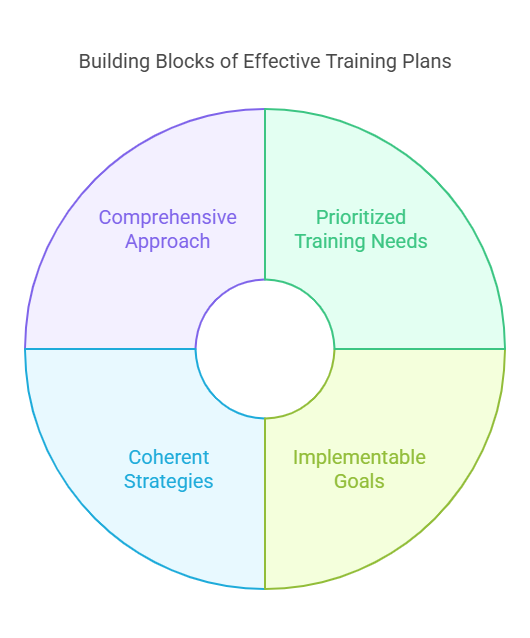
Key Principles of Effective Training Plans
This part details the foundational principles that should guide the creation and implementation of training plans. It emphasizes the importance of prioritizing, ensuring plans are feasible, coherent in their goals and methods, and comprehensive enough to address both current and future needs.
Prioritized Training Needs
Effective training plans begin by identifying and prioritizing needs based on their value to the business, the difficulty of implementation, and the urgency of the training. This prioritization helps in focusing resources on training that promises the most significant impact on performance and business outcomes.
Implementable Goals
For a training plan to be successful, its goals must be realistic and achievable. Each objective should be carefully scrutinized against potential obstacles, ensuring that the plans laid out are feasible within the given resources and timelines.
Coherent Strategies
The training strategy should clearly outline the methods and actions planned to achieve the set goals. This includes a detailed roadmap of training activities, tools, and resources that will be used to enhance the skills and knowledge of the workforce.
Comprehensive Approach
A robust training plan is expansive and anticipates future needs. It not only addresses immediate skill gaps but also focuses on developing long-term competencies that will prepare employees to meet upcoming challenges and industry changes.
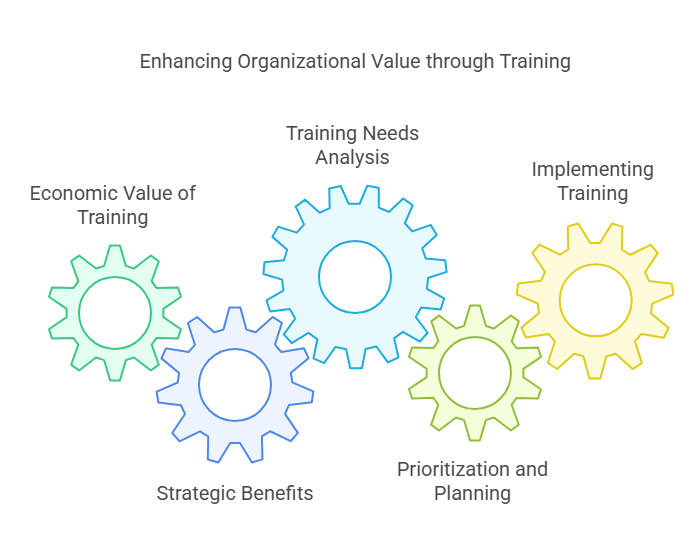
Adding Value Through Training
This part explains how training programs add value to the organization by potentially increasing economic benefits through improved efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance in various processes.
Economic Value of Training
Training is an investment that should ultimately lead to an increase in economic value for the company. This can be through direct outcomes like increased productivity or indirect benefits such as improved employee retention.
Strategic Benefits of Training
Strategic training enhances various aspects of pharmaceutical operations, such as speeding up patient recruitment, reducing data management errors, and improving compliance with clinical protocols. Each training initiative should be linked to specific strategic benefits that align with business goals.
Training Needs Analysis
This segment focuses on how to identify current competencies, determine skill gaps, and plan the necessary training interventions.
Identifying Skills and Gaps
This step involves a thorough assessment of current skills available versus the skills needed. Techniques such as interviews, surveys, and performance reviews can help identify these gaps accurately.
Effective Data Collection Methods
Using a combination of data collection methods ensures a comprehensive understanding of existing competencies and areas needing improvement. Structured interviews, focus groups, and feedback from performance audits are valuable tools for this purpose.
Gap Analysis and Reporting
After collecting and analyzing data, the next step is to perform a gap analysis to pinpoint precise skill deficiencies. Reporting these findings should include potential solutions and training programs designed to bridge the identified gaps.
Prioritization and Planning
This part covers how to manage and prioritize identified training needs effectively.
Training Gap Analysis
Using tools such as attractiveness-implementation difficulty grids helps in prioritizing training needs effectively. This analysis helps in understanding which training programs will provide the most value with the least difficulty in implementation.
Major Changes vs. Continuous Improvements
Distinguishing between needs that require major changes and those that necessitate continuous improvements allows for better allocation of resources and more strategic planning.
Implementing Training Initiatives
Focuses on the execution of training priorities and managing them effectively.
Strategic Training Priorities
Selecting a few key priorities for implementation at any given time can prevent resource dilution and focus efforts on areas with the potential for the highest impact.
Stakeholder Analysis
Understanding the perspectives and influence of different stakeholders involved in training programs is crucial. This analysis helps in aligning training initiatives with both internal expectations and external requirements.
Role of Management in Training
Discusses the critical roles that both senior management and the training department play in the training process.
Management's Involvement
Senior management must be actively involved in the training process, from planning to execution. Their support is essential in legitimizing the training efforts and aligning them with business objectives.
Training Department's Role
The training department should act as an advisor and facilitator, ensuring that the training programs are effectively meeting the needs identified. They should also maintain a supportive role, allowing line managers to take ownership of the implementation.
Sourcing Training Strategies
This section deals with how to source and implement training resources effectively.
Internal vs. External Training Resources
Choosing between internal and external training resources depends on the specific needs identified. Internal resources are often more tailored to the company's operations, while external resources can bring in new perspectives and expertise.
Selecting External Trainers
When external trainers are necessary, they should be selected based on their expertise in the pharmaceutical field, their training effectiveness, and their ability to tailor their programs to the company's specific needs.
Explore Our Courses
Courses Available:
Conclusion
In conclusion, a successful training strategy is critical for achieving 'World Class' standards in clinical research. By aligning training initiatives with business goals and effectively managing resources, pharmaceutical companies can significantly enhance their operational efficacy. Incorporating a blend of internal and external resources, and ensuring active management participation are key components. Organizations like CCRPS play a pivotal role in setting benchmarks and providing resources that can be utilized to elevate training programs. Continual evaluation and adaptation of the training strategy will ensure that it remains effective and relevant.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
The key components include identifying and prioritizing training needs, ensuring the goals are realistic and implementable, outlining clear strategies, and adopting a comprehensive approach that prepares employees for current and future challenges.
-
Training adds value by improving operational efficiency, enhancing compliance with regulatory standards, accelerating clinical processes like patient recruitment, and increasing employee retention and satisfaction, all of which contribute to the economic value of the company.
-
Effective methods include structured interviews, surveys, focus groups, and performance audits. These tools help in accurately assessing current competencies and identifying skill gaps.
-
Senior management plays a crucial role in legitimizing and supporting training initiatives. Their involvement ensures that training efforts are aligned with the strategic goals of the company and adequately resourced.
-
Training needs are prioritized based on their strategic importance, urgency, and the difficulty of implementation. Tools like the attractiveness-implementation difficulty grid can help in making these determinations.
-
What is the importance of external trainers in pharmaceutical training strategies?
-
Training strategies should be reviewed and updated regularly, at least annually, or as major changes in technology, regulations, or market conditions occur. This ensures that the training remains relevant and aligned with the company’s needs.
-
Training has a significant impact on compliance and regulatory affairs by ensuring that employees are aware of and understand the latest regulatory requirements and industry standards. Effective training reduces the risk of non-compliance and enhances the quality of clinical data and research outcomes.