The Role of GCP in Ensuring Clinical Trial Integrity
Good Clinical Practice (GCP) is a cornerstone of ethical and scientific standards in clinical research. It ensures that clinical trials are conducted with integrity, prioritizing participant safety and producing reliable data. In 2025, as clinical trials become more complex and data-driven, adherence to GCP principles is more critical than ever.
Related Blog: What Is Good Clinical Practice?
How GCP Ensures the Reliability of Trial Data?
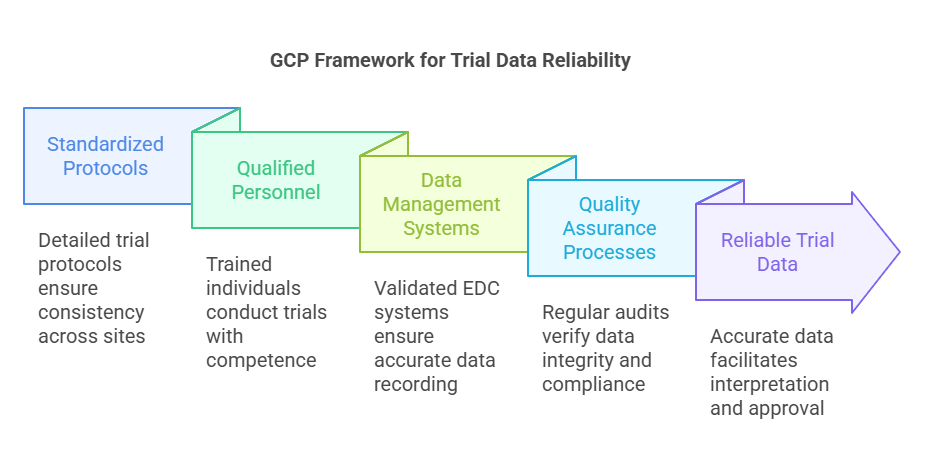
GCP provides a framework that guarantees the credibility and accuracy of data collected during clinical trials.
Key Measures:
Standardized Protocols: GCP mandates the use of detailed trial protocols outlining objectives, methodologies, and procedures, ensuring consistency across study sites.
Qualified Personnel: Clinical trials must be conducted by individuals with appropriate education, training, and experience, ensuring competent execution of the study.
Data Management Systems: Implementation of validated electronic data capture (EDC) systems with audit trails ensures data is accurately recorded and traceable.
Quality Assurance Processes: Regular monitoring and audits are conducted to verify data integrity and compliance with the study protocol.
These measures collectively uphold the reliability of trial data, facilitating accurate interpretation and regulatory approval.
Related Blog: Top Benefits of GCP Training for Healthcare Professionals
Preventing Data Manipulation and Fraud
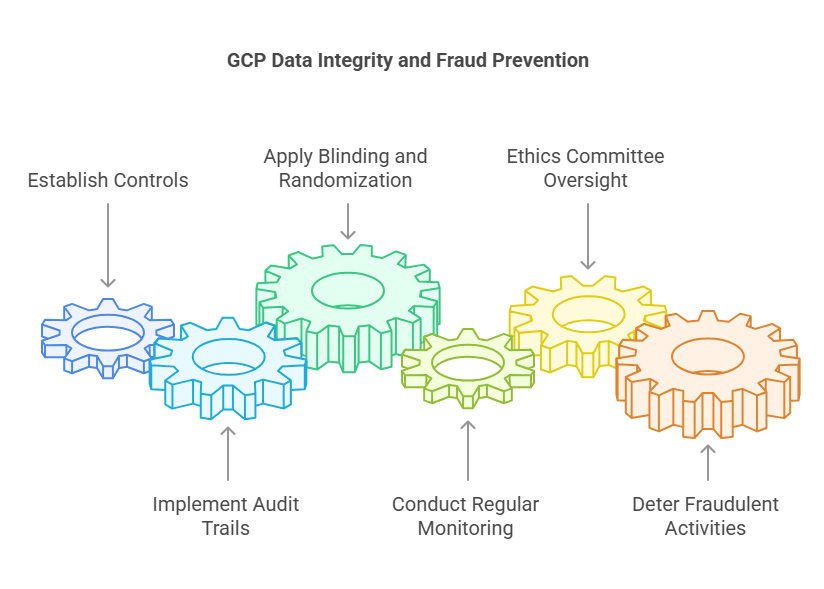
GCP establishes stringent controls to prevent data manipulation and fraud, safeguarding the integrity of clinical research.
Preventive Strategies:
Audit Trails: All data entries and modifications are logged, providing a transparent record of data handling.
Blinding and Randomization: Implementing blinding and randomization reduces bias and prevents intentional data alteration.
Regular Monitoring: Continuous oversight by monitors ensures adherence to protocols and identifies discrepancies promptly.
Ethics Committee Oversight: Independent review boards evaluate study conduct, adding an additional layer of scrutiny.
These mechanisms deter fraudulent activities and promote trust in clinical trial outcomes.
Importance of Informed Consent and Ethical Considerations
Informed consent is a fundamental ethical requirement in clinical research, ensuring participants are fully aware of the study's nature and implications.
Ethical Imperatives:
Comprehensive Information: Participants receive detailed explanations of the study's purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits.
Voluntary Participation: Consent is obtained without coercion, respecting the autonomy of individuals.
Ongoing Communication: Participants are kept informed of any new information that may affect their willingness to continue.
Protection of Vulnerable Populations: Special considerations are made for groups with limited capacity to consent, ensuring ethical inclusion.
These practices align with the Declaration of Helsinki, reinforcing the ethical conduct of clinical trials.
Ensuring Accurate Record-Keeping and Reporting
Accurate documentation is vital for the credibility and reproducibility of clinical trials.
Documentation Standards:
Comprehensive Records: All trial-related activities, including informed consent, data collection, and adverse events, are meticulously documented.
Secure Data Storage: Data is stored securely, maintaining confidentiality and preventing unauthorized access.
Timely Reporting: Findings and safety reports are submitted promptly to regulatory authorities and stakeholders.
Retention Policies: Records are retained for specified periods, facilitating audits and future reference.
These practices ensure transparency and accountability throughout the research process.
Regulatory Audits and GCP Compliance
Regulatory audits assess compliance with GCP standards, ensuring the integrity of clinical trials.
Audit Processes:
Inspection of Documentation: Regulators examine trial records to verify adherence to protocols and regulatory requirements.
Facility Assessments: Clinical sites are evaluated for proper infrastructure and operational procedures.
Personnel Interviews: Staff are interviewed to assess their understanding and implementation of GCP principles.
Corrective Actions: Identified deficiencies are addressed through corrective and preventive action plans.
Regular audits reinforce compliance and enhance the credibility of clinical research.
Related Blog: GCP Certification: What You Need to Know?
10 Lesser-Known Facts About GCP
Global Harmonization: GCP guidelines are internationally recognized, facilitating multi-country clinical trials. (Source)
Evolving Standards: GCP is periodically updated to incorporate advances in research methodologies and ethical considerations.
Training Requirements: All clinical trial personnel must undergo GCP training, ensuring consistent understanding and application. (Source)
Risk-Based Monitoring: GCP encourages risk-based approaches to monitoring, focusing resources on critical study aspects.
Electronic Signatures: GCP accepts electronic signatures, streamlining documentation processes.
Patient-Centric Approaches: GCP supports incorporating patient perspectives into trial design and conduct.
Data Transparency: GCP promotes the sharing of clinical trial data, enhancing scientific collaboration.
Post-Trial Access: GCP emphasizes providing participants with access to beneficial treatments after trial completion.
Cultural Sensitivity: GCP encourages cultural considerations in trial conduct, respecting local customs and practices.
Environmental Considerations: GCP acknowledges the environmental impact of clinical trials, promoting sustainable practices.
Conclusion
Good Clinical Practice (GCP) plays a vital role in ensuring the integrity of clinical trials by establishing ethical standards, promoting data reliability, and safeguarding participant rights. By enforcing strict protocols and ethical considerations, GCP helps prevent data manipulation, ensures accurate reporting, and maintains transparency throughout the trial process. With evolving technologies and regulatory frameworks, GCP continues to be essential in upholding the credibility and success of clinical research. At CCRPS, we are committed to adhering to GCP standards to deliver high-quality, ethical clinical trials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
GCP ensures the ethical conduct of clinical trials, protecting participant safety and rights while maintaining the reliability and accuracy of the trial data.
-
GCP implements robust mechanisms like audit trails, blinding, randomization, and continuous monitoring to prevent data manipulation and ensure integrity.
-
Informed consent ensures that participants are fully aware of the trial's nature, risks, and benefits, allowing them to voluntarily decide whether to participate.
-
Regulatory audits assess adherence to GCP standards, ensuring that clinical trials are conducted according to established protocols, thereby verifying the reliability of trial data.
-
GCP requires comprehensive and secure documentation of all trial-related activities, ensuring transparency, traceability, and accountability throughout the clinical trial process.