Everything You Need to Know About CROs
Buckle up! We're diving into the world of Clinical Research Organizations (CROs), the unsung heroes of the pharmaceutical universe. Forget capes and masks; these organizations wield paperwork and data like no other. Ready to unravel the secrets of CROs and discover how they’re transforming medicine behind the scenes? Let's get this adventure started!
What Exactly is a CRO?
A Clinical Research Organization (CRO) plays a very important role in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries, performing in a full service capacity and being capable of taking charge of almost all of the tasks that are related to research and development (R&D) of new drugs and medical devices. These organizations are the backbone of clinical trials, as having a backstage crew is essential to a smooth running theater production.
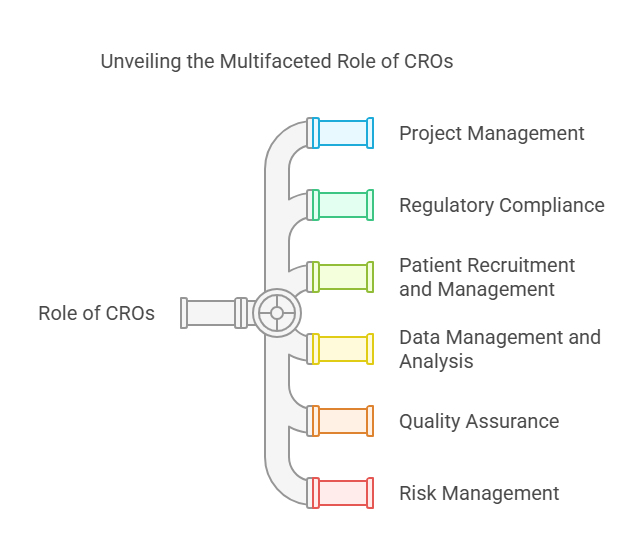
Role of CROs in Drug Development:
Project Management: Clinical Research Organizations (CROs) are in charge of administering the end to end clinical trial management. This entails planning, executing, monitoring and closing out trials. They guarantee that every stage of the trial is carried out in conformity with the set protocol and within the set time frame.
Regulatory Compliance: Clinical trials must comply with regulatory standards, hence the need of CRO. CROs are familiar with the legal systems of the countries where the trials are held. They manage the submission of the trial to the regulatory authorities and guarantee that the trial is conducted in conformity with the regulations of the country and/or internationally such as the FDA and EMA.
Patient Recruitment and Management: A major challenge in clinical trials is recruiting and retaining participants who meet the study’s criteria. Strategies are employed by CROs to recruit participants efficiently and manage them once enrolled in the study through to the end of the study, including adherence to the trial protocol and follow-ups.
Data Management and Analysis: CROs collect a vast amount of data during clinical trials. This data needs to be meticulously managed and analyzed to ensure its integrity. CROs use sophisticated data management systems to store, manage, and analyze clinical data. This is crucial for determining the efficacy and safety of the drug or device being tested.
Quality Assurance: CROs guarantee the correct execution of every aspect of the trial and the accuracy of the data generated by implementing quality assurance processes. Audits and regular inspections are performed to adhere to Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines.
Risk Management: Another key responsibility of CROs is identifying, assessing, and managing risks that are associated with clinical trials. They also employ risk management strategies to mitigate potential issues that could impact the trial’s outcomes which they identify, assess and manage.
Advantages of Using CROs:
Expertise and Specialization: CROs bring specialized knowledge and experience that pharmaceutical companies might not have in-house. This includes expertise in managing multi-site trials, handling specific therapeutic areas, and navigating complex regulatory landscapes.
Cost-Effectiveness: By outsourcing to CROs, drug manufacturers can reduce costs associated with staffing, training, and maintaining an in-house team for clinical trials.
Scalability: CROs can scale their services up or down based on the project’s requirements, providing flexibility that is difficult to achieve internally.
Speed: CROs can often accelerate the pace of trials by leveraging their resources and expertise, potentially leading to faster drug development timelines.
In essence, CROs are integral to the development of new medical treatments, handling the intricate and critical tasks required to move a drug from concept to market. Their role is indispensable in ensuring that new therapies are both effective and safe for public use, all while adhering to stringent regulatory standards.
Future Outlook of CROs
From being valued at a whopping $3.37 billion in 2017, the pharmaceutical outsourcing market is sprinting towards an estimated $7.26 billion by 2024. Why the meteoric rise? Simple: efficiency and specialization. Companies like LabCorp and IQVIA are leading the charge, transforming drug development with precision and expertise that only dedicated organizations can offer.
Links: https://introspectivemarketresearch.com/reports/formulation-development-outsourcing-market/
Why the Buzz Around CROs?
Think of CROs as the elite task forces of healthcare. They’re equipped to handle the complexities of drug approval processes, from ensuring compliance with global regulations to conducting meticulous trials that can stand up to scrutiny from bodies like the FDA. Their neutrality is their superpower—unbiased and focused, they provide the credible data needed to push medical innovation to the next stage.
10 Lesser Known Facts about CRO
Clinical Research Organizations (CROs) are key players in the pharmaceutical and biotech industries, but beyond their well-known roles in managing clinical trials, there are several lesser-known aspects that highlight their critical influence and unique capabilities in the field. Here are ten lesser-known facts about CROs:
Pioneering Remote and Virtual Trials: CROs are at the forefront of implementing decentralized clinical trials, which use digital technologies to conduct studies remotely. This approach reduces the need for participants to visit trial sites frequently, expanding the potential pool of participants and increasing convenience.
Involvement in Veterinary Medicine: CROs are not limited to human medicine; they also play a significant role in the development of veterinary drugs and treatments. They conduct clinical trials for a range of animal species, which is crucial for advancing veterinary medicine.
Disaster Response Research: Some CROs specialize in conducting research related to disaster response, such as developing and testing medical countermeasures for bioterrorism or pandemic outbreaks, ensuring rapid deployment of effective interventions during emergencies.
Global Health Initiatives: CROs often collaborate on global health challenges, including neglected tropical diseases that are prevalent in developing countries but have limited market incentives for research and development. They work with government bodies, non-profit organizations, and international health agencies to develop treatments for these conditions.
Advanced Bioinformatics: CROs employ advanced bioinformatics techniques to manage and analyze vast amounts of biological data. This capability is crucial in the era of personalized medicine and genomics, where data complexity and volume can be overwhelming.
Early Involvement in Medical Device Innovation: Beyond pharmaceuticals, CROs are integral to the development and testing of new medical devices, from wearable health monitors to advanced surgical tools, ensuring these innovations meet regulatory standards and are clinically effective.
Eco-Friendly Research Practices: Increasingly, CROs are adopting sustainable and eco-friendly practices in their operations to minimize environmental impact. This includes using electronic data capture systems to reduce paper use and implementing green technologies in their facilities.
Cognitive Computing and AI: Some CROs are integrating cognitive computing and AI technologies to revolutionize the way clinical trials are designed and conducted. These technologies can predict patient enrollment patterns, identify potential risks, and optimize trial protocols.
Cultural and Linguistic Adaptation: For global trials, CROs often undertake extensive cultural and linguistic adaptations of trial materials to ensure that they are appropriate and understandable for diverse participant groups, which is critical for ethical compliance and effective communication.
Philanthropic Research Programs: Certain CROs engage in philanthropic research programs, providing their services free or at cost to research diseases that are rare or primarily affect underfunded regions. These programs often focus on diseases that are not typically profitable but have significant impacts on public health.
Conclusion
Ever dreamed of donning a lab coat and impacting lives globally? CROs offer a plethora of roles ripe for the taking, from Clinical Research Coordinators to Data Analysts. No experience? No problem! Institutions like CCRPS are your gateway to this thriving industry, offering certifications that pave the way to becoming a clinical research guru.
CCRPS offers esteemed certifications that prepare individuals for impactful careers in clinical research. These include the Good Clinical Practice Certification, Clinical Research Coordinator Certification, and Clinical Research Associate Certification. Each program is designed to equip professionals with the knowledge and skills necessary to uphold the highest standards of clinical research and contribute significantly to medical advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
CROs optimize R&D by managing the multifaceted phases of clinical trials, allowing pharmaceutical companies to focus on innovation rather than administrative burdens.
-
Advanced technologies like AI and machine learning are revolutionizing how CROs analyze data, predict outcomes, and ensure accuracy, propelling the industry towards more reliable and quicker drug approvals.
-
Absolutely! By accelerating drug trials and ensuring safety, CROs have a direct impact on how quickly new treatments reach patients worldwide, especially in areas affected by rare diseases.
-
Dynamic, diverse, and critical. Whether you’re in project management, regulatory affairs, or patient recruitment, your work directly contributes to medical advancements that can change the world.
-
Regulatory complexity and high standards for trial data integrity continue to challenge CROs, demanding constant adaptation and innovation.
-
Strict ethical guidelines and clear separation of operational duties ensure CROs can provide unbiased, accurate trial results.
-
Expect more personalized medicine approaches, precision in trial design, and integration of real-world data to refine the efficacy of clinical trials.
-
It reduces costs, decreases time to market for new drugs, and allows pharma companies to leverage specialized expertise without maintaining a full-scale research department.
-
The most crucial stage is typically Phase III, where the drug is tested on a larger population to assess its efficacy and safety comprehensively.
-
CROs ensure rigorous adherence to ethical standards and regulatory requirements, prioritizing patient safety and the integrity of trial results.
-
While costs vary, hiring a CRO can significantly reduce overall expenses related to drug development by streamlining processes and minimizing infrastructural investments.
-
Globalization allows CROs to conduct multicentric trials, facilitating quicker data collection and more diverse patient data, enhancing the drug approval process's efficiency and efficacy.













CRC exam prep tips